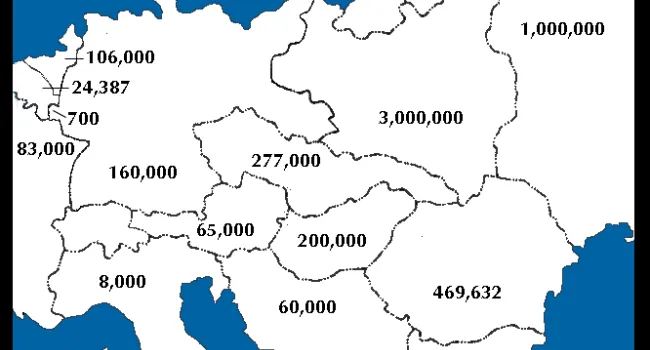
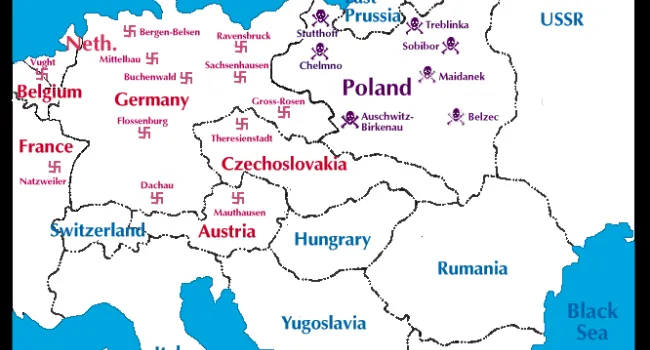
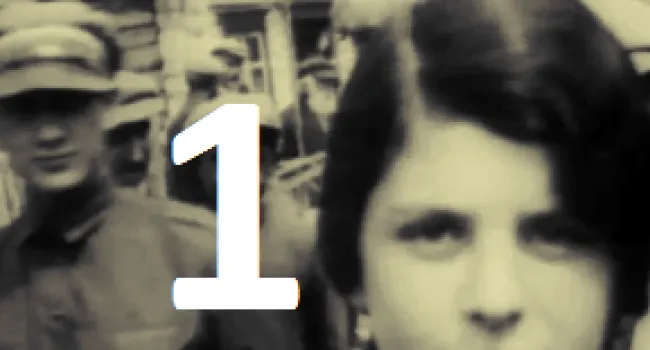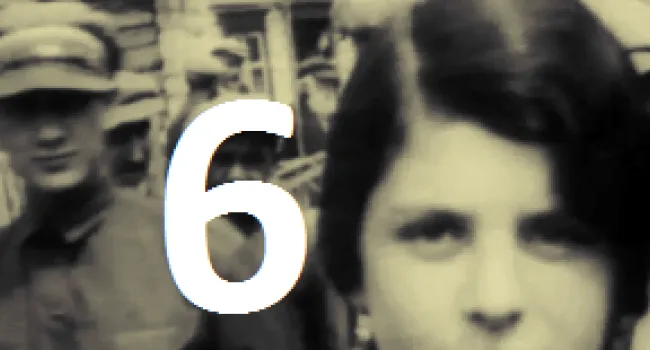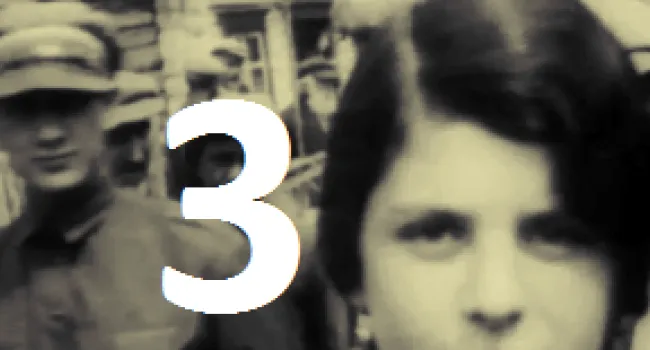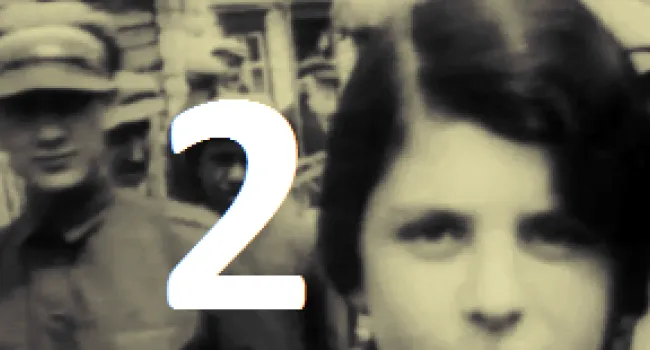Born in Cologne, Germany, in 1925, Rudy Herz heard of Hitler in school when, in 1935, textbooks took on a Germanic nationalistic slant, the Swastika flag was flown, and Jews lost privileges. His family was moved to a Jewish ghetto; the living conditions were horrible. Finally, the Herz family was sent to Auschwitz in sealed cattle cars. Some relatives never resurfaced. The conditions in the camp were desperate—surrounded by guards, people were starving, slowly being destroyed by inhuman work or the crematorium. There was no greenery, no life, no dignity. Germans told Jewish prisoners that before it was over, they would die. "Americans don't know what it's like to starve for years," Herz says. He lived with the constant sound of screams. In 1945 the prisoners were liberated and told, "You are free; the Americans are behind you." He was reunited with his brother and settled in Myrtle Beach. His experiences still haunt him. "I have survivors' guilt; my soul stays in a crematorium with victims at Auschwitz."
Standards
- 5.3 Demonstrate an understanding of the economic, political, and social effects of World War II, the Holocaust, and their aftermath (i.e., 1930–1950) on the United States and South Carolina.
- 6.5.CE Explain the impact of nationalism on global conflicts and genocides in the 20th and 21st centuries.
- 7-4 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the causes and effects of world conflicts in the first half of the twentieth century.
- The influence of both world wars and the worldwide Great Depression are still evident. To understand the effects these events had on the modern world, the student will utilize the knowledge and skills set forth in the following indicators:
- 7-4.5 Summarize the causes and course of World War II, including drives for empire, appeasement and isolationism, the invasion of Poland, the Battle of Britain, the invasion of the Soviet Union, the "Final Solution," the Lend-Lease program, Pearl Harbo...
- 7-4.6 Analyze the Holocaust and its impact on European society and Jewish culture, including Nazi policies to eliminate the Jews and other minorities, the Nuremberg trials, the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the rise of nationalism in Southwest...
- The influence of both world wars and the worldwide Great Depression are still evident. To understand the effects these events had on the modern world, the student will utilize the knowledge and skills set forth in the following indicators:
- 8.5.CO Compare South Carolina and U.S. wartime contributions and demobilization after World War II.
- This indicator is intended to encourage inquiry into the significant causes of World War I and the impacts of the Treaty of Versailles, including its failure to prevent future global conflicts.
- USHC-7 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the impact of World War II on the United States and the nation’s subsequent role in the world.