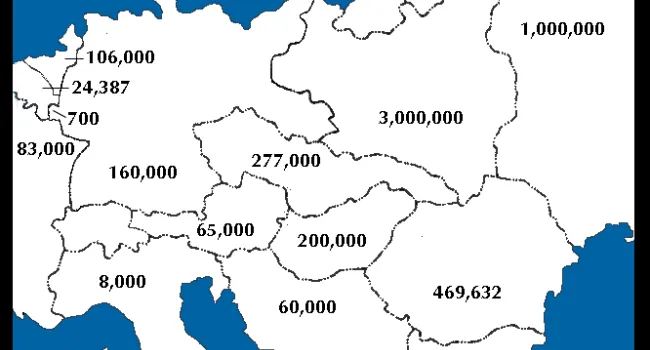
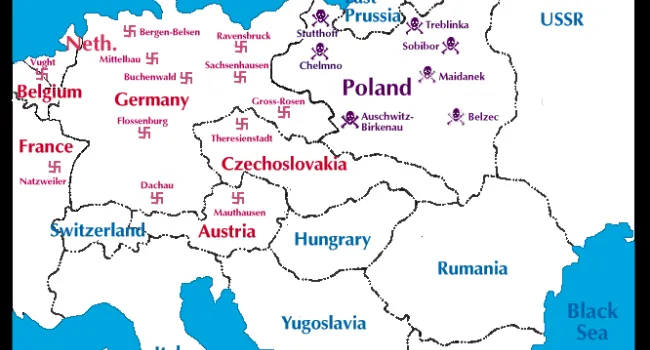
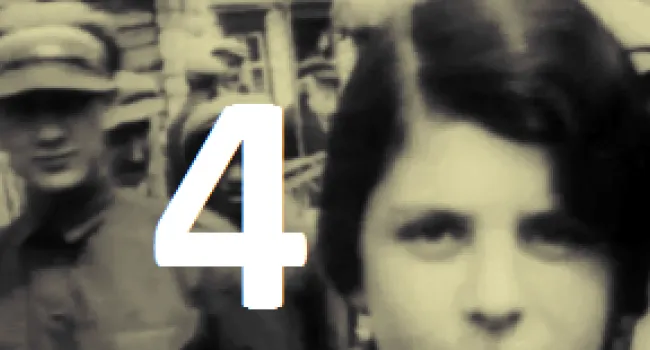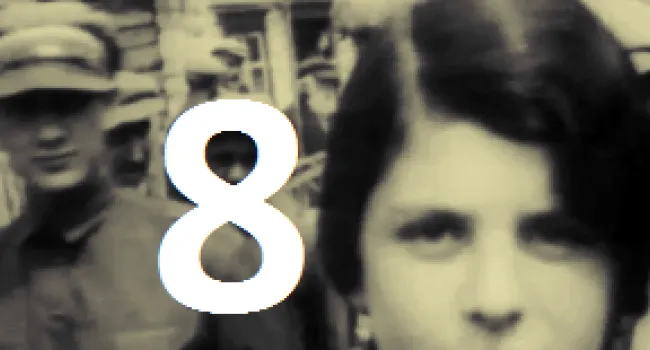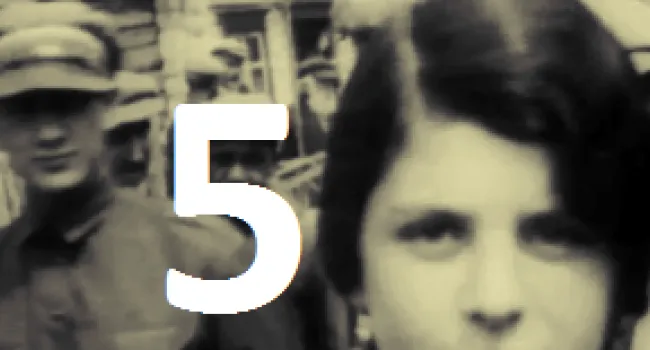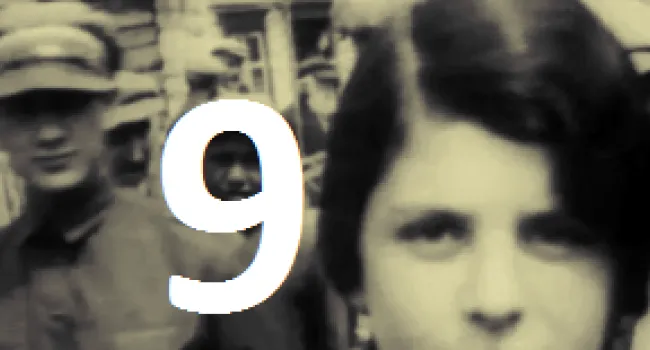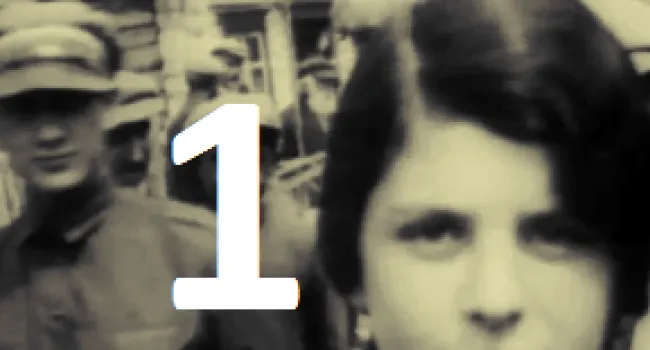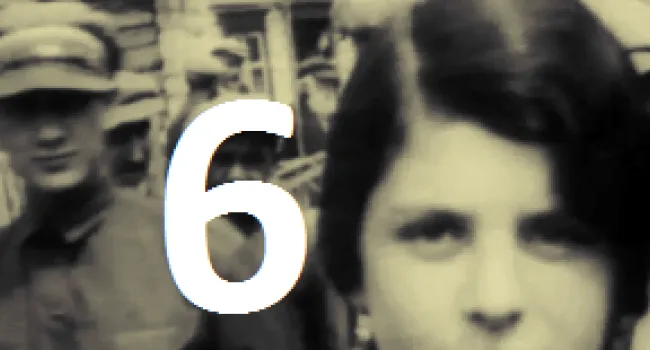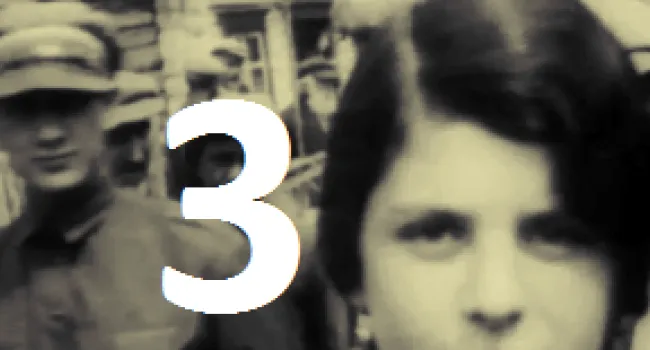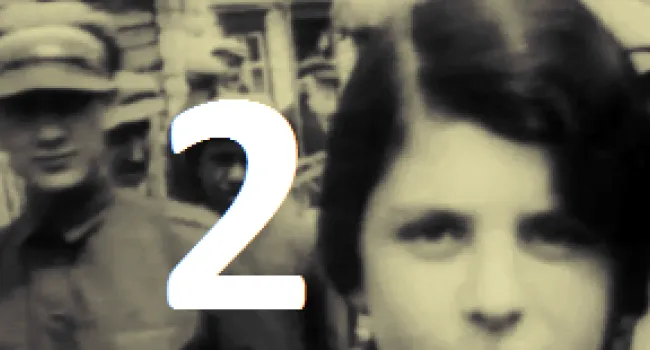Luba Goldberg nee Schreibman was born in 1921 in Romania, not far from Russia. Her family contained many well-respected Romanian doctors. With Romania part of the WWII German Axis, it enacted the same anti-Jewish laws as were enacted in Germany, taking away all Jewish property and businesses and putting Jews in ghettos. Any Jew who did not work was deported to a concentration camp to be killed. Luba's mother was killed trying to escape to Russia. Her brother began the Bucharest office of The Joint Jewish Distribution Committee, the American/Jewish organization which helped Jews to leave or get medical help, food, or housing. Shortly after the war, Luba left Communist Romania and went through a British Displaced Persons camp on Cyprus (where she met her husband, Bernard, a Polish Holocaust survivor whom the British sent to Cyprus after capturing him in an attempt to illegally immigrate into then British-controlled Palestine) and then to Israel soon after the establishment of the State in 1948.. She and her husband and two children ultimately immigrated to Columbia, S.C., where he worked in Lourie's Department Store before they bought a series of motels together. With the help of Senator Fritz Hollings, she was able to bring her Holocaust-survivor sister and niece to Columbia from Argentina. She always cherished the opportunity to live in America.
Standards
- 5.3 Demonstrate an understanding of the economic, political, and social effects of World War II, the Holocaust, and their aftermath (i.e., 1930–1950) on the United States and South Carolina.
- 6.5.CE Explain the impact of nationalism on global conflicts and genocides in the 20th and 21st centuries.
- 8.5.CO Compare South Carolina and U.S. wartime contributions and demobilization after World War II.
- This indicator is intended to encourage inquiry into the significant causes of World War I and the impacts of the Treaty of Versailles, including its failure to prevent future global conflicts.