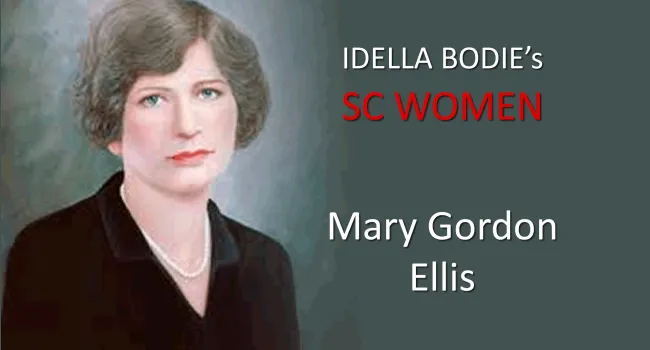Vocabulary
- Abolish – to do away with
- Abolition – the termination of slavery in the United States
- Abolitionist – one who works to terminate slavery in the United States
- Equal rights – having the same value and rights as another
- Emancipation – to free from oppression, bondage, or restraint; liberate Human rights – characteristic of mankind and the rights of all people
- Law – a rule established by authority, society, or custom; the body or system of such rules
- Lawyer – one whose profession is to give legal advice and assistance to clients in court or in other legal matters
- Slave – one bound in servitude to a person or household as an instrument of labor
- Slavery – bondage to a master or household
- Underground Railroad – a secret network of cooperation aiding fugitive slaves in reaching sanctuary in the free states
Classroom Activities
Related to the study of the abolition of slavery and equal rights for all
Although these are different types of movements, many of the people and concepts overlap in their search for human rights for all.
Biographies: Select from the listing below a famous person who played an important role in the abolition of slavery. Design a biography of the individual as a report or display.
Anthony Burns, Lydia Maria Child, Frederick Douglass, William Lloyd Garrison, Sarah and Angelina Grimke’, Julia Ward Howe, Samuel J. May, Lucretia Mott, Wendell Phillips, William Seward, Harriet Beecher Stowe, Arthur and Lewis Tappan, Sojourner Truth, Theodore Dwight Weld
Compare and Contrast Historical Perspective: Compare and contrast the life of a slave on a Southern plantation with a Northern free man. Discuss in class.
Research: Individual students or small groups. With each topic, list the facts about the document and the impact that it had on The United States at the time.
Fugitive Slave Law from the Missouri Compromise of 1820, Compromise of 1850, Gag Rule, Underground Railroad, Bill of Rights
Research: When did President Lincoln free the slaves? What impact did the Emancipation Proclamation have on the North and the South?
Analysis: Why did the Wilmot Proviso threaten to fuel sectional tensions in Congress? How might such a bill have either caused or created an imbalance of power in Congress?
Debate: Debate the conflicting role of women in the 1800’s. How did the attitudes toward women impact social, culture and historical perspectives of that time.
Biographies: Select from the listing below a famous person who played an important role in the fight for equal rights. What contributions did she make to the equal rights movement for women? How did her contribution impact our life today?
Susan B. Anthony, Julia Ward Howe, Martha Moore Ballard, Anne Hutchinson, Elizabeth Blackwell, Lucretia Mott, Matilda Joslyn Gage, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Angelina Grimke’, Mercy Otis Warren
Resources
You need to be logged in to listen to view this content. Create an account now; it's quick, easy, and free!
Log In to ViewVocabulario
- Abolir – eliminación
- Abolición – la terminación de la esclavitud en los Estados Unidos
- Abolicionista: uno que trabaja para poner fin a la esclavitud en los Estados Unidos
- Igualdad de derechos: tener el mismo valor y derechos que otros
- Emancipación – liberarse de la opresión, la esclavitud o la restricción; liberar los derechos humanos – características de la humanidad y los derechos de todas las personas
- Ley – una norma establecida por la autoridad, la sociedad o la costumbre; el cuerpo o sistema de dichas normas
- Abogado – profesión que da asesoramiento legal y asistencia a los clientes en los tribunales o en otros asuntos legales
- Esclavo – alguien atado en servidumbre a una persona o hogar como un instrumento de trabajo
- Esclavitud – esclavitud a un amo o hogar
- Ferrocarril subterráneo (Underground Railroad) – una red secreta de cooperación que ayuda a los esclavos fugitivos a llegar al santuario en los estados libres
Actividades en el aula
Relacionado con el estudio de la abolición de la esclavitud y la igualdad de derechos para todos
Aunque se trata de diferentes tipos de movimientos, muchas de las personas y conceptos coinciden en su búsqueda de derechos humanos para todos.
Biografías: Seleccione de la lista a continuación una persona famosa que tuvo un importante papel en la abolición de la esclavitud. Crear un informe o presentación de la biografía del individuo.
Anthony Burns, Lydia Maria Child, Frederick Douglass, William Lloyd Garrison, Sarah y Angelina Grimke', Julia Ward Howe, Samuel J. May, Lucretia Mott, Wendell Phillips, William Seward, Harriet Beecher Stowe, Arthur y Lewis Tappan, Sojourner Truth, Theodore Dwight Weld
Comparar y contrastar la perspectiva histórica: Comparar y contrastar la vida de un esclavo en una plantación del sur con un hombre libre del norte. Utilizarlo como tema de discusión en clase.
Investigación: Estudiantes individuales o pequeños grupos. Con cada tema, enumere los hechos sobre el documento y el impacto que tuvo en Los Estados Unidos en ese momento.
Ley de Esclavos Fugitivos del Compromiso de Missouri de 1820, Compromiso de 1850, Regla Mordaza, Ferrocarril Subterráneo, Carta de Derechos
Investigación: ¿Cuándo liberó el presidente Lincoln a los esclavos? ¿Qué impacto tuvo la Proclamación de Emancipación en el Norte y el Sur?
Análisis: ¿Por qué la Wilmot Proviso amenazó con alimentar las tensiones seccionales en el Congreso? ¿Cómo podría un proyecto de ley de este tipo haber causado o creado un desequilibrio de poder en el Congreso?
Debate: Debate sobre el papel contradictorio de la mujer en los años 1800. ¿Cómo impactó las actitudes hacia las mujeres las perspectivas sociales, culturales e históricas de la época?
Biografías: Seleccione de la lista a continuación una persona famosa que jugó un papel importante en la lucha por la igualdad de derechos. ¿Qué contribuciones hizo al movimiento por la igualdad de derechos para las mujeres? ¿Cómo impactó su contribución nuestra vida hoy en día?
Susan B. Anthony, Julia Ward Howe, Martha Moore Ballard, Anne Hutchinson, Elizabeth Blackwell, Lucretia Mott, Matilda Joslyn Gage, Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Angelina Grimke', Mercy Otis Warren.